Brig. Gen H.H. Sibley
Brig. Gen H.H. Sibley
On January 3, 1862, Confederate brigadier general, Henry Hopkins Sibley left El Paso with a little more than three regiments of mounted Texans. This brigade, which he called the Confederate Army of New Mexico, totaled 2,510 officers and men. He headed north, with the intention of defeating the Union forces at Fort Craig, capturing the capital city of Santa Fe, taking the heavily provisioned Fort Union, and then marching into Colorado to take control of the gold and silver mines before finally heading westward to conquer California. If his plan had succeeded, Sibley would have fulfilled the Confederacy’s dreams of Manifest Destiny while giving the south warm water ports on the Pacific and a huge boost to its treasury.
 Col. E.R.S. Canby
Col. E.R.S. Canby
Sibley arrived at Fort Craig in the middle of February. Scouts, fooled by Canby’s use of “Quaker cannons,” logs painted black to imitate artillery pieces, reported that the fort was too heavily fortified to be taken. Hoping to lure the Federals into the open, Sibley moved his men into an arroyo south of the fort. The cautious Canby refused to be provoked.
 The black line on the horizon is Contadoria Mesa. The battle happened just to the left of it.
The black line on the horizon is Contadoria Mesa. The battle happened just to the left of it.  Lt. Colonel William Read Scurry
Lt. Colonel William Read Scurry
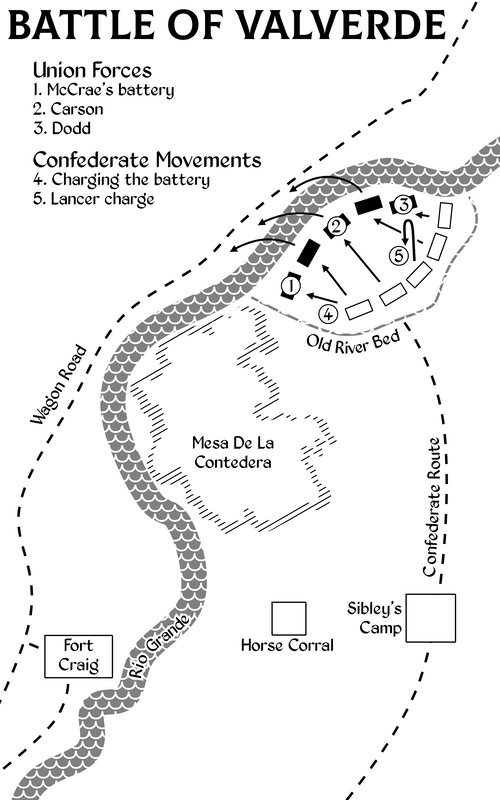
As the day progressed, more soldiers arrived on both sides of the battle line. Colonel Benjamin S. Roberts reinforced the Union cavalry with the 5th New Mexico Infantry. When Colonel Canby arrived with most of Fort Craig’s remaining garrison, he ordered all but First New Mexico Volunteers under Carson and the Second New Mexico Volunteers under Colonel Miguel Piño to cross to the eastern side of the river.
 Maj Lockridge
Maj Lockridge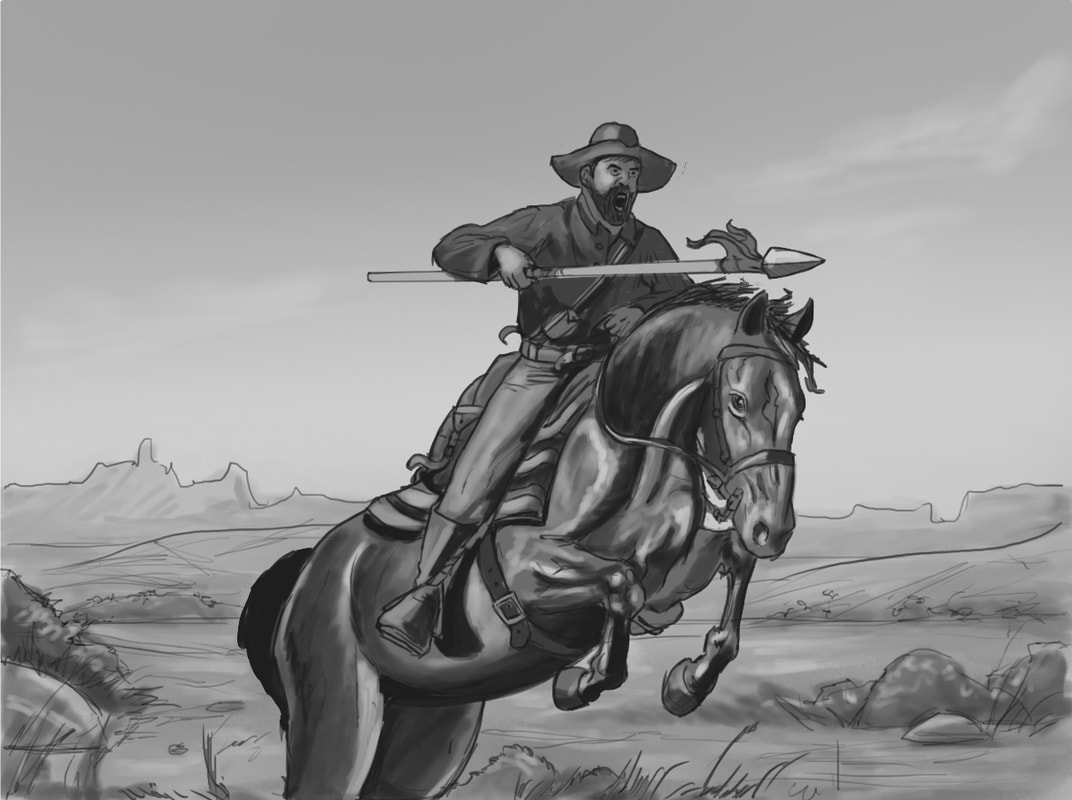  Illustration by Ian Bristow in Where Duty Leads.
Illustration by Ian Bristow in Where Duty Leads.  An etching from a Harper's Weekly showing McRae defending his guns.
An etching from a Harper's Weekly showing McRae defending his guns.  Illustration by Ian Bristow, from Where Duty Calls.
Illustration by Ian Bristow, from Where Duty Calls.